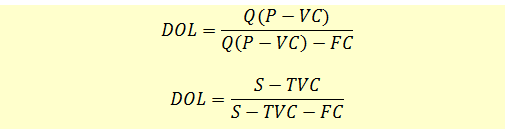
In other words, operating leverage is the measure of fixed costs and their impact on the EBIT of the firm. In the table above, sales revenue increased by 10% ($62,500 to $68,750). However, it resulted in a 25% increase in operating income ($10,000 to $12,500). It does this by measuring how sensitive a company is to operating income sales changes. Higher measures of leverage mean that a company’s operating income is more sensitive to sales changes. Yes, industries that are reliant on expensive infrastructure or machinery tend to have high operating leverage.
Would you prefer to work with a financial professional remotely or in-person?
If a company expects an increase in sales, a high degree of operating leverage will lead to a corresponding operating income increase. But if a company is expecting a sales decrease, a high degree of operating leverage will lead to an operating income decrease. As a business owner or manager, it is important to be aware of the company’s cost structure and how changes in revenue will impact earnings.
- Degree of operating leverage closely relates to the concept of financial leverage, which is a key driver of shareholder value.
- Operating Leverage is a financial ratio that measures the lift or drag on earnings that are brought about by changes in volume, which impacts fixed costs.
- The reason operating leverage is an essential metric to track is because the relationship between fixed and variable costs can significantly influence a company’s scalability and profitability.
- Your profitability is supercharged by high DOL when business conditions and economic circumstances are favorable.
- Because retailers sell a large volume of items and pay upfront for each unit sold, COGS increases as sales increase.
Degree of Operating Leverage: Definition, Formula & Calculation
With each dollar in sales earned beyond the break-even point, the company makes a profit, but Microsoft has high operating leverage. Financial and operating leverage are two of the most critical leverages for a business. Besides, they are related because earnings from operations can be boosted by financing; meanwhile, debt will eventually be paid back by those increased earnings. On the other hand, if the case toggle is flipped to the “Downside” selection, revenue declines by 10% each year, and we can see just how impactful the fixed cost structure can be on a company’s margins. Revenue and variable costs are both impacted by the change in units sold since all three metrics are correlated. Therefore, each marginal unit is sold at a lesser cost, creating the potential for greater profitability since fixed costs such as rent and utilities remain the same regardless of output.
Formula for Operating Leverage
For example, if funds are raised through long-term debts such as bonds and debentures, these instruments carry fixed charges in the form of interest. In fact, financial leverage relates to financing activities (i.e., the cost of raising funds from different sources carrying fixed charges or not involving fixed charges). We will also see the calculation of the degree of operating leverage for an alternative formula considered an ideal calculation method. For illustration, let’s say a software company has invested $10 million into development and marketing for its latest application program, which sells for $45 per copy. By analyzing DOL, stakeholders can better anticipate the impacts of sales fluctuations on a company’s profitability. Let us take the example of Company A, which has clocked sales of $800,000 in year one, which further increased to $1,000,000 in year two.
Otherwise, add the specific period data in the section “Period to period specific data” above. For the particular case of the financial one, our handy return of invested capital calculator can measure its influence on the business returns. Starting out, the telecom company must incur substantial xero promo code coupons february 2021 by anycodes upfront capital expenditures (Capex) to enable connectivity capabilities and set up its network (e.g., equipment purchases, construction, security implementations). An example of a company with a high DOL would be a telecom company that has completed a build-out of its network infrastructure.

Get in Touch With a Financial Advisor
A financial professional will offer guidance based on the information provided and offer a no-obligation call to better understand your situation. Our writing and editorial staff are a team of experts holding advanced financial designations and have written for most major financial media publications. Our work has been directly cited by organizations including Entrepreneur, Business Insider, Investopedia, Forbes, CNBC, and many others. Finance Strategists is a leading financial education organization that connects people with financial professionals, priding itself on providing accurate and reliable financial information to millions of readers each year.
The more fixed costs there are, the more sales a company must generate in order to reach its break-even point, which is when a company’s revenue is equivalent to the sum of its total costs. This ratio indicates that the higher the degree of financial leverage, the more volatile earnings will be. Since interest is usually a fixed expense, leverage magnifies returns and EPS. This is good when operating income is rising, but it can be a problem when operating income is under pressure.
The company spent tens of millions of dollars to develop each of its digital delivery and storage software programs. But thanks to the internet, Inktomi’s software could be distributed to customers at almost no cost. After its fixed development costs were recovered, each additional sale was almost pure profit. In contrast, a company with relatively low degrees of operating leverage has mild changes when sales revenue fluctuates. Companies with high degrees of operating leverage experience more significant changes in profit when revenues change.
High operating leverage can be risky for a company in several ways, including reduced flexibility, magnified effects of revenue changes, financial risk, and strategic risk. This section will use the financial data from a real company and put it into our degree of operating leverage calculator. If you try different combinations of EBIT values and sales on our smart degree of operating leverage calculator, you will find out that several messages are displayed. But this comes out to only a $9mm increase in variable costs whereas revenue grew by $93mm ($200mm to $293mm) in the same time frame. In addition, in this scenario, the selling price per unit is set to $50.00, and the cost per unit is $20.00, which comes out to a contribution margin of $300mm in the base case (and 60% margin). If sales and customer demand turned out lower than anticipated, a high DOL company could end up in financial ruin over the long run.
A 10% increase in sales will result in a 30% increase in operating income. A 20% increase in sales will result in a 60% increase in operating income. Consequently it also applies to decreases, e.g., a 15% decrease in sales would result to a 45% decrease in operating income.
Leave a Reply